BNA Annual General Meeting 2025
1st April 2025

We are excited to share these neuroscience in schools toolkits, which are designed to:
- give neuroscientists the materials they need to be able to carry out effective, age-appropriate outreach sessions in schools
- enable teachers to run inspiring, interactive classes based on current neuroscience research
- equip parents and carers to run activities for home-learning
Each toolkit focuses on a particular topic in neuroscience, and includes a PowerPoint presentation and an accompanying information sheet. The sessions also include age-appropriate, engaging activities that reinforce the concepts taught.
Many of the topics have two versions of toolkit: one developed for primary school children (ages ~ 5-11, Key Stages 1-3) and another for secondary school / sixth form students (ages ~12-18, Key Stages 4 and 5).
Each session is self-contained but one can also mix and match different topics and activities as desired. Some examples of mixed sessions, e.g. for visiting school groups and school leavers' destinations days, are below:
We are also very excited to be able to provide links to two further sets of external resources developed for schools:
 Summary: The brain enables us to do everything that we do, think and feel, and it is made up of cells called neurons, which connect to each other and are key to brain function. We can look at neurons through a microscope.
Summary: The brain enables us to do everything that we do, think and feel, and it is made up of cells called neurons, which connect to each other and are key to brain function. We can look at neurons through a microscope.
Activities: Scientist says, make a pipe cleaner neuron
Materials needed: Pipe cleaners of different colours and sizes
Resources:
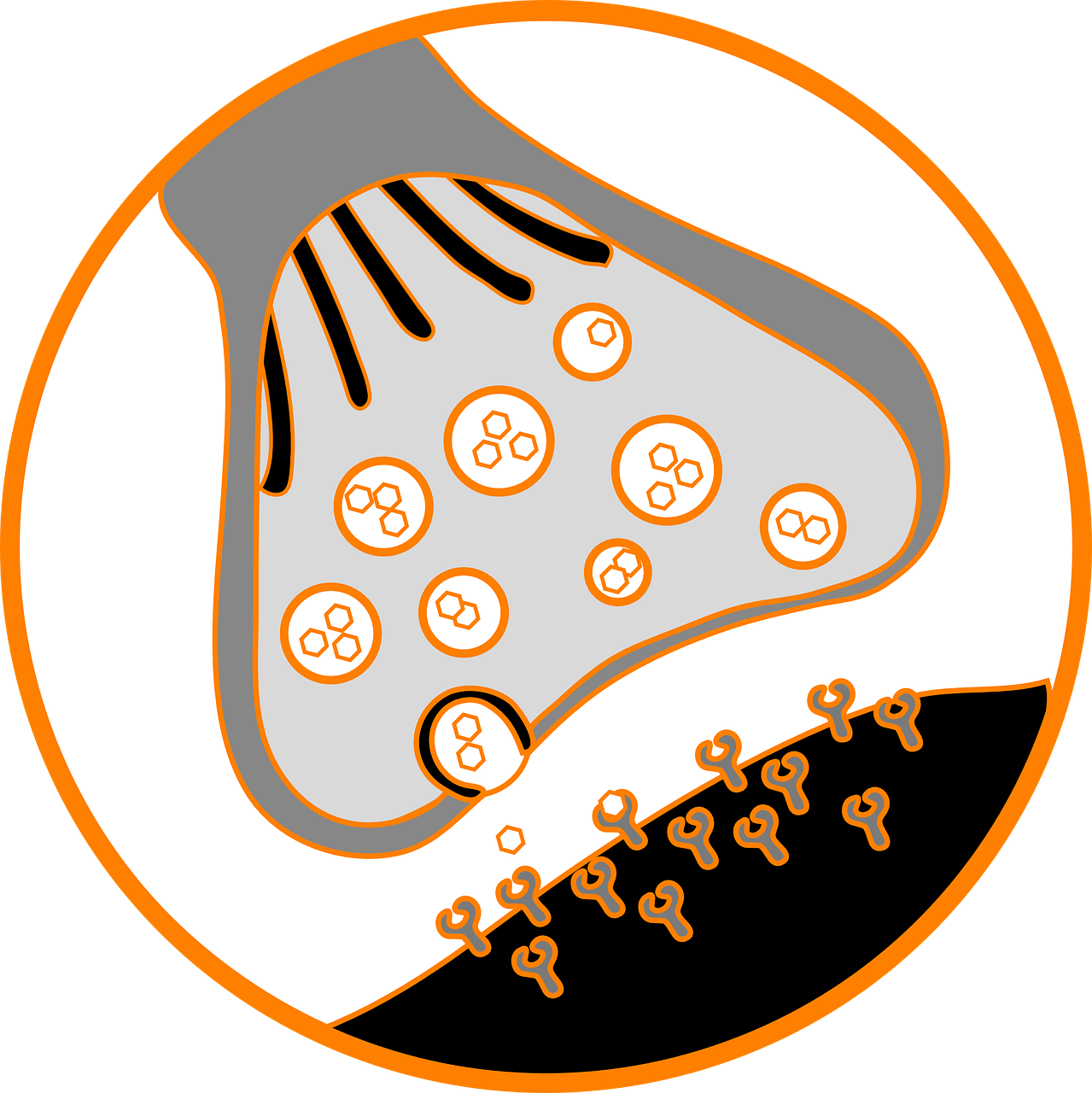 Summary: Neurons are the cells in the brain, they connect and communicate with one another. The way in which neurons 'talk' to each other is key to brain function. Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical messages.
Summary: Neurons are the cells in the brain, they connect and communicate with one another. The way in which neurons 'talk' to each other is key to brain function. Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical messages.
Activities: Neuronal communication
Materials needed: Bubbles (with wands to blow through)
Resources:
 Summary: The nervous system allows the brain to communicate with the rest of the body, and it has two main parts, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
Summary: The nervous system allows the brain to communicate with the rest of the body, and it has two main parts, the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
Activities: Nervous system
Materials needed: Sticky notes/ pens and paper, string
Resources:
 Summary: What the terms memory and learning mean, how learning leads to memories being stored in the brain, and some of the different types of memories.
Summary: What the terms memory and learning mean, how learning leads to memories being stored in the brain, and some of the different types of memories.
Activities: Scientist says, memory game, bendy pencil
Materials needed: Pencils and paper
Resources:
 Summary: What scientists are, what they look like and wear, and what skills and atributes you might need to become a scientist.
Summary: What scientists are, what they look like and wear, and what skills and atributes you might need to become a scientist.
Activities: Chicken, fox, and a bag of grain & Scientist race
Materials needed: Lab coats, goggles and gloves
Resources:
 Summary: Explore what medicines are and where they come from in terms of all the different people involved in their discovery and development.
Summary: Explore what medicines are and where they come from in terms of all the different people involved in their discovery and development.
Activities: Where do medicines come from role play
Materials needed: Bandages/plasters, lab coat/ stethoscopes/goggles, clipboard/ paper pad, pen/pencil, high Vis vest, hard hat, camouflage/safari hat
Resources:
 Summary: Discussing key ethical questions regarding research and artificial intelligence such as reading minds, changing memories and what the advantages and disadvantages would be of robots becoming as smart as humans.
Summary: Discussing key ethical questions regarding research and artificial intelligence such as reading minds, changing memories and what the advantages and disadvantages would be of robots becoming as smart as humans.
Activities: Group discussions on different ethical questions surrounding science advancement
Materials needed: None required
Resources:
 Summary: The brain is the source of our feelings, it creates our emotions, which can be affected by our experiences. Things we can do to keep our brain healthy, and where/ who to go to for help if we are sad.
Summary: The brain is the source of our feelings, it creates our emotions, which can be affected by our experiences. Things we can do to keep our brain healthy, and where/ who to go to for help if we are sad.
Activities: Beach scenario, Draw your experiences and emotions, Body scan
Materials needed: Pencils/pens and paper
Resources:
 Summary: How we can look at the brain, parts of the brain, parts of the neuron, how neurons communicate and an introduction to cells that assist neurons.
Summary: How we can look at the brain, parts of the brain, parts of the neuron, how neurons communicate and an introduction to cells that assist neurons.
Age: Please note that this session probably works best for young students up to the age of 16
Activities: Microscopy/ Electrical muscle stimulator (EMS) activity/ Make a pipe cleaner neuron
Materials needed: Microscopes and slides/ EMS or TENS device/ pipe cleaners
Resources:
 Summary: Neurons connect and communicate with one another within neuronal networks. The stages of the action potential as electrical signals travel along a neuron, and the chemical transmission of messages betwen neurons via the synapse.
Summary: Neurons connect and communicate with one another within neuronal networks. The stages of the action potential as electrical signals travel along a neuron, and the chemical transmission of messages betwen neurons via the synapse.
Activities: Neuron race
Materials needed: Baskets/bucket and balls (that fit into the baskets)
Please click here to access the resources for this session.
 Summary: The Nervous System is divided into the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). The PNS is further divided into other branches leading to the sympathetic and parasympathetic subdivisions which control our involuntary actions.
Summary: The Nervous System is divided into the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). The PNS is further divided into other branches leading to the sympathetic and parasympathetic subdivisions which control our involuntary actions.
Activities: Knee jerk relfex (For help watch this video), reaction time
Materials needed: 30cm long rulers, pencils and paper
Resources to download:
 Summary: How scientists study the brain, the hemispheres of the brain and a detailed look at the different lobes and other regions of the brain and their functions
Summary: How scientists study the brain, the hemispheres of the brain and a detailed look at the different lobes and other regions of the brain and their functions
Activities: Mirror drawing activity/ build a brain model/ parietal lobe experiment
Materials needed: A carboard box, mirror, coloured marker and pieces of paper with a large shape printed on them/ paper, scissors, gluesticks/ callipers or bent paperclips
Resources to download:
 Summary: Introduction to the brain, and the terms learning and memory. The different memory stores, why and how the brain stores information.
Summary: Introduction to the brain, and the terms learning and memory. The different memory stores, why and how the brain stores information.
Activities: Memory game
Materials needed: no extra materials required
Resources:
 Summary: What sorts of molecules drugs are and how they work, the stages and processes of drug discovery and clinical trials, the placebo effect and licensing.
Summary: What sorts of molecules drugs are and how they work, the stages and processes of drug discovery and clinical trials, the placebo effect and licensing.
Activities: Placebo effect activity, optional receptor/drug activity
Age: Please note, some concepts in this session may be challenging for younger secondary-school-aged children to understand and the session may need to be adapted slightly or allowed more time for explanation.
Materials needed: 2 tubs of hand cream, optional: (item with a hole/indentation in it e.g. cookie-cutter/glue stick, and modeling clay/ play-dough)
Resources:
 Summary: Discussing key ethical questions regarding research and artificial intelligence such as reading minds, changing memories and what the advantages and disadvantages would be of robots becoming as smart as humans.
Summary: Discussing key ethical questions regarding research and artificial intelligence such as reading minds, changing memories and what the advantages and disadvantages would be of robots becoming as smart as humans.
Activities: Group discussions on different ethical questions surrounding science advancement
Materials needed: None required, although you may wish to split the class into small discussion groups and provide them with markers and sugar paper to brainstorm their ideas and views
Resources:
 Summary: Brain development during the teenage years regarding different brain areas and explaining the process of synaptic pruning. The behaviours that arise during this development such as the sense of self and risk taking.
Summary: Brain development during the teenage years regarding different brain areas and explaining the process of synaptic pruning. The behaviours that arise during this development such as the sense of self and risk taking.
Activities: Egg game and/or balloon game
Materials needed: Eggs and/or balloons
Resources to download:
![]() Summary: Introducing students to drugs and the neuroscience behind how drugs affect the brain and neuronal communication. How drug abuse can lead to drug addiction and what happens in the brain for this to occur.
Summary: Introducing students to drugs and the neuroscience behind how drugs affect the brain and neuronal communication. How drug abuse can lead to drug addiction and what happens in the brain for this to occur.
Activities: Mouse Party game, Addiction card game
Materials needed: Pack of cards
Resources:
Upper Secondary (ages 15-18)